 Return list
Return list
Pneumatic actuator selection
Please confirm valve torque before using pneumatic actuator. And increase the safety value on the torque, water steam or non-lubricating liquid medium increase 25% safety value; Non-lubricating slurry liquid medium increase by 30% safety value.
Double acting pneumatic actuator selection example
The selected valve torque is 210NM, the air source pressure is only 5bar, the medium is non-lubricated water steam, taking into account the safety factors, increase the safety value of 25% namely 262NM, according to the double action output torque table to find the corresponding torque value of the air source pressure at 5bar. 277NM should be selected, model POADA300
Working diagram of double acting pneumatic actuator
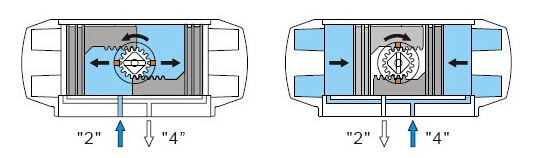
When the air source pressure from the air port (2) into the cavity between the two pistons of the cylinder, the two pistons separate to move to the direction of the cylinder at both ends, forcing the compression of the spring at both ends, the air at both ends of the air chamber is discharged through the air port (4), and the two plug rack synchronous drive output shaft (gear) rotation in the counterclockwise direction. After the air source pressure is reversed through the solenoid valve, the two pistons of the cylinder move to the middle direction under the elastic force of the spring, the air in the middle air chamber is discharged from the air port (2), and the two piston rack synchronously drives the output shaft (gear) to rotate clockwise. (If the piston is installed in the opposite direction, the output shaft will rotate in reverse when the spring is returned)
Pneumatic actuator torque table
|
Cylinder diameter mm |
2.5bar |
3.0bar |
3.5bar |
4.0bar |
4.5bar |
5.0bar |
5.5bar |
6.0bar |
7.0bar |
8.0bar |
|
POADA20 |
8.3 |
10 |
11.6 |
13.3 |
15 |
16.6 |
18.3 |
19.9 |
23.3 |
26.6 |
|
POADA40 |
14.7 |
17.6 |
20.5 |
23.5 |
26.4 |
29.3 |
32.2 |
35.2 |
41 |
46.9 |
|
POADA80 |
29.1 |
34.9 |
40.7 |
46.5 |
52.3 |
58.2 |
64 |
69.8 |
81.4 |
93 |
|
POADA130 |
45.7 |
54.9 |
64 |
73.2 |
82.3 |
91.5 |
101 |
110 |
128 |
146 |
|
POADA200 |
66.5 |
79.7 |
93 |
106 |
120 |
133 |
146 |
160 |
186 |
213 |
|
POADA300 |
138 |
166 |
194 |
221 |
249 |
277 |
304 |
332 |
387 |
443 |
|
POADA500 |
217 |
261 |
304 |
348 |
391 |
434 |
478 |
521 |
608 |
695 |
|
POADA850 |
283 |
340 |
397 |
453 |
510 |
567 |
623 |
680 |
793 |
907 |
|
POADA1200 |
383 |
459 |
536 |
612 |
689 |
765 |
842 |
918 |
1071 |
1224 |
|
POADA1750 |
531 |
638 |
744 |
850 |
956 |
1063 |
1169 |
1275 |
1488 |
1700 |
|
POADA2500 |
935 |
1122 |
1309 |
1496 |
1683 |
1870 |
2057 |
2244 |
2618 |
2992 |
|
POADA4000 |
1347 |
1617 |
1886 |
2156 |
2425 |
2695 |
2964 |
3234 |
3772 |
4311 |
The performance characteristics of pneumatic actuator are mainly:
1. The rated output force or torque of the pneumatic device shall comply with the provisions of GB/T12222 and GB/T12223.
2, in the no-load case, the cylinder input according to the specified pressure, its action should be smooth, no jamming and crawling phenomenon;
3. Under the air pressure of 0.6MPa, the output torque or thrust of the pneumatic device in both directions of opening and closing shall be no less than the value marked by the pneumatic device label, and the action shall be flexible, and permanent deformation and other abnormal phenomena shall not be allowed in each part;
4. When the maximum working pressure is used for the seal test, the air leakage from the respective back pressure side is not allowed to exceed (3+0.15D) cm3/min (standard state); Air leakage from the end cover and output shaft is not allowed to exceed (3+0.15d) cm3/min;
5, the strength test with 1.5 times the maximum working pressure test, maintain the test pressure for 3 minutes, the cylinder body end cover and static sealing parts are not allowed to have leakage and structural deformation;
6, the number of operation life, pneumatic device simulation pneumatic valve action, in the case of maintaining the output torque or thrust capacity of two directions, the number of opening and closing operation should not be less than 50000 times (start-closing cycle for one);
7, pneumatic device with buffer mechanism, when the piston movement to the stroke terminal position, is not allowed to appear impact phenomenon;
The torque required to open and close the valve determines the output torque of the electric actuator, which is generally proposed by the user or selected by the valve manufacturer. As the actuator manufacturer, it is only responsible for the output torque of the actuator. The torque required for normal opening and closing of the valve is determined by the valve diameter size, working pressure and other factors, but because of the processing precision and assembly process of the valve manufacturer, Therefore, the torque required by different manufacturers of the same specifications of valves is different, even if it is the same specification of valves produced by the same valve manufacturers are different. When selected, the torque selection of the actuator is too small, it will cause the failure to open and close the valve normally, so the pneumatic actuator must choose a reasonable torque range.